Cloud and security of precious data
- Home
- Blog
- Clouds For Business
- Cloud and security of precious data
Why is this article needed?
This article is written for those who want to understand in general how safe it is to work with the virtual cloud (and with any data over the Internet) in terms of information protection. Whenever possible, we tried not to dig into technical details, but for those who are interested in this, there are links to interesting and useful materials on the topic (not always "two in one").
Network security: a battlefield or a well-established mechanism?
To understand how dangerous or safe working with data over the Internet is. Firstly, it is necessary to determine the basic terminology and conceptually understand what happens when working with the cloud. Next, we will analyze the individual components of this process and their interaction, also indicating the necessary mechanisms for organizing correct work. After that, we will show the classic "fails" that bring to naught the functioning of debugged systems and conclude with philosophical reflections about the line between logical actions and paranoia.
Cosmic scale! Main entities and their interaction
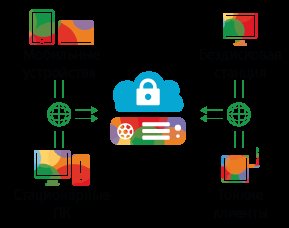
In general, working with any data over the network looks like this (Fig. 1): in point A there is a server on which certain data is stored and processed, and in points B, C, D, etc. - user devices from which this data is entered and on which it is processed (sometimes) and displayed. To communicate with A, information transmission channels are used.
The level below: disassembling the blocks
Data center
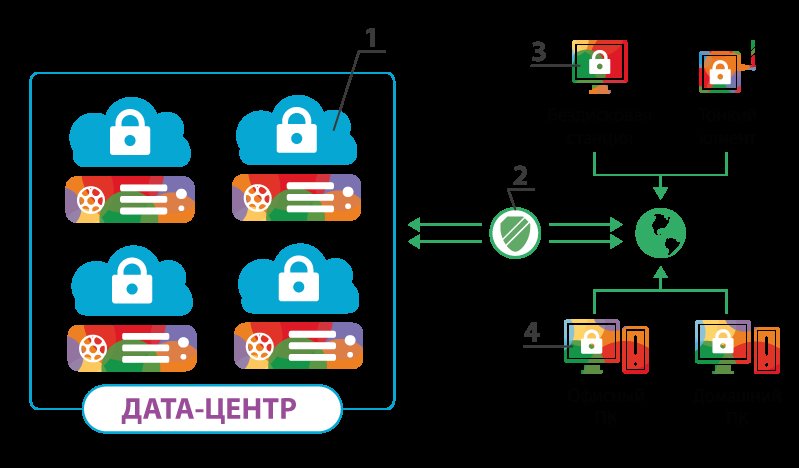
Perhaps the most secure block is the most remote from the user - the virtual machine in a data center (item 1 in Fig. 2). Why? Firstly, the data center business itself is built on the use of highly reliable equipment (fault tolerance, reservation, etc.), and data center specialists are professionals focused on performing specific tasks. It is almost impossible to achieve the same level of functioning at “home”. Secondly, data itself is protected both from interference by data center employees (see below the information on virtualization and disk encryption) and from theft/seizure by, let us say dishonest competitors; since the perimeter and the data center itself are protected no worse (and sometimes even better) than respectable banks.
By the way, if you think about it, banks and data centers have quite a lot in common: for example, at the dawn of the banking industry, it was considered strange to give your money for storing in a strange structure instead of leaving them in an apartment in a stocking. Does this remind anything? Now information is quite solid currency, and the same measures are being taken to protect it as to protect other assets. Virtual machines (vaults) in the data center (bank), opened with a personal key, are used for storage. Secure data transmission channels act as cash-in-transit vehicles, and computer security specialists act as "security guards".
Recommendations on the use of data access devices (computers, smartphones, thin clients) can easily be found "similar" to recommendations for using bank cards. "Do not disclose your password (even to provider's employees)" = "Keep your PIN code secret (even from bank employees)". "Do not use free Wi-Fi" = "Check an ATM for the presence of readers". "If something went wrong or there are doubts, call the provider" = "Remember the phone number of the bank's hotline", etc.
The Internetнет
The next block is about data transmission channels (item 2 in Fig. 2). If we compare with the banking sector, then here we determine how the money will be transported: with the help of a cash-in-transit vehicle or by public transport. In the Internet security terminology, secure transport (protocol) is IPsec, public transport is ordinary IP. In the banking sector, in addition to a protected car, it is also desirable to use a secret route of movement. Its IT counterpart is a virtual private network (VPN). What does this mean? This means that even if an attacker somehow intercepts the information ("cash-in-transit vehicle"), they will find that the data is encrypted ("in a cash box"), and the decryption key is not here, it is with the data owner.
Diskless user devices
And finally, user devices. There are possible options here, depending on requirements to computing power (for example, analyzing large amounts of data, calculating programs, etc. is more logical to use a server, and for web surfing and documents, a weak smartphone or tablet is often enough) and data storage (storing a corporate database on employees’ computers is probably impractical). Very often (especially in a corporate environment) user devices do not have a hard disk at all (item 3 in Fig. 2) and are used only for entering, processing, and displaying information. In such cases, disconnecting a device from a power source breaks the communication channel with the server and access to information.
Devices with disk drives
If the user device has a storage device (memory card, hard disk, etc.), it must be encrypted (see below), access to it has to be locked with a password, and beacons and various anti-theft programs can be installed on the device itself (item 4 in Fig. 2) (as examples, the hardware that some business laptops are equipped with, as well as common anti-theft software for smartphones). It is also worth mentioning the process of turning on the device and accessing information. Keep in mind that your device may not be turned on by you, and if such an opportunity is provided, make it difficult for an attacker to access the system (complex passwords, readers of fingerprints or retinas, tokens, and other means of user identification).
The devil is in the details, or how not to burn on the little things
- Who offers a cheaper price: a manufacturer or dealer?
- A guard!
It seems that everyone knows about this, but still, the main fails happen not on the hardware but on the human level. It does not matter how good the encryption scheme is, if the access password is written on a piece of paper, next to a workplace, or if it can be taken from an employee/secretary/admin.
If you do not know what social engineering is, then we recommend you acquaint yourself. If you know, but for some reason, you forgot, then we recommend using distributed two- and more-tiered systems, when access to a source of classified information (laptop, person, password) does not mean automatic access to all information in a readable form.
Information protection? What is it?
- Vladimir Petrovitch, good afternoon! It's FSB bothering you.
- I know.
- From where?
- You've reached me on a switched-off mobile phone.
The main thing when increasing the levels of protection, implementing cryptographic algorithms, complex passwords, and intricate security policies is to stop in time (see recommended literature), of course, unless your business is the introduction of such systems. Why? Because everything can be hacked. The only question is hacker capabilities. If the foreign intelligence service of one of the neighboring states wants to find out the number of bananas on your secretary's virtual farm, they will do it. But this does not mean that you need to forget about security and encryption. Not at all! After all, in addition to intelligence services, some lower-ranking detractors have a lower level of intelligence and not so powerful capabilities. But the basic methods described above are very adequate protection against them.
If you are obsessed with conspiracy theories, and security measures at all levels are the things that take up most of your working time, we strongly recommend the following publications. After reading them, there are two possible options: either you will grow to believe that everyone is watching everyone (and, alas, we will not change your mind), or you will decide that appropriate security measures when you reasonable trust in professionals and calmly move to the clouds (if you have not already done so).
By the way, from our experience of participating in specialized events and communicating with clients: skeptics used to say that clouds would not take root, because our people are used to keeping all the information close at hand. But, as it turned out, our people need ACCESS to information. Permanent, convenient, from anywhere. But KEEPING IT CLOSE AT HAND could lead to some consequences. C'est la vie!
Literature
Actually, this article was originally about specific encryption techniques and algorithms, but they are so well described in Wikipedia that we decided to leave it here. If you need more detailed technical or mathematical advice, please contact us, we will answer in detail.
| BitLocker | Disk encryption software (can be used both on user devices and on servers with virtual machines) |
| TrueCrypt | Another good encryption program |
| IPsec | Secure data transfer protocol |